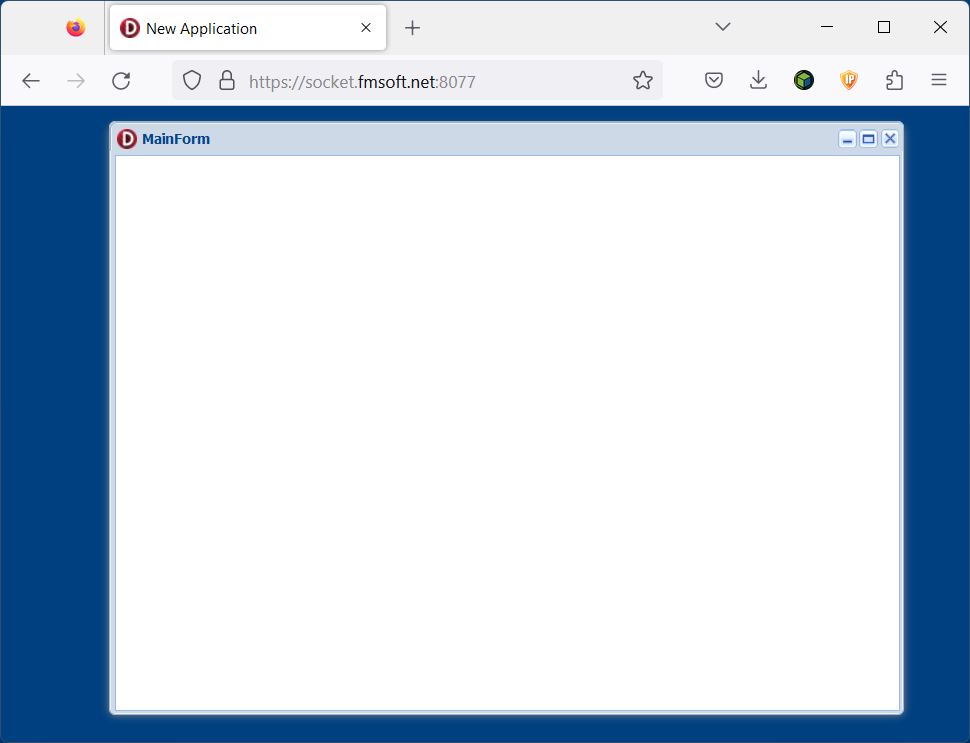
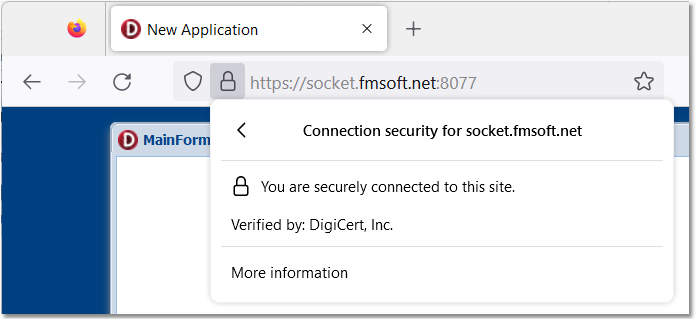
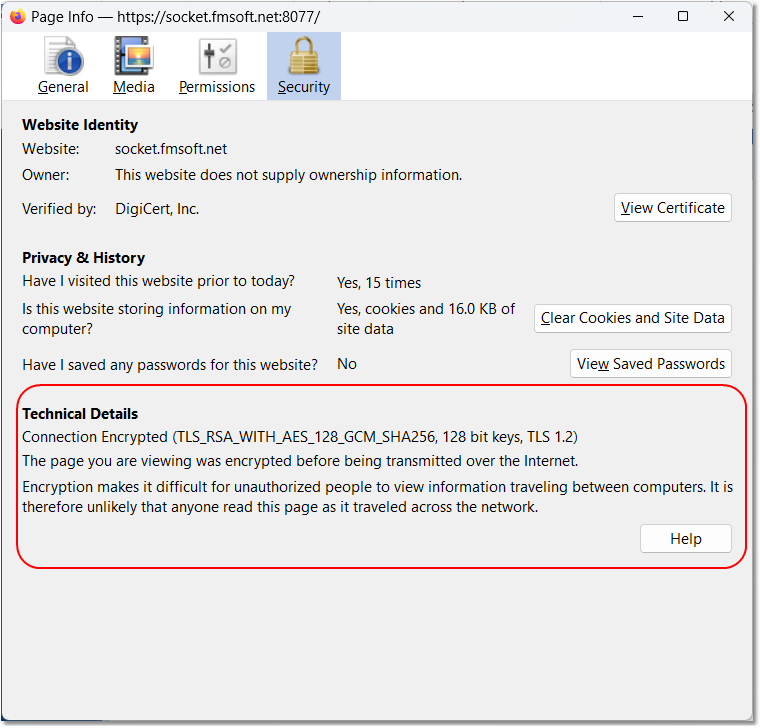
Testing the Certificate Locally
1
1. Redirect the domain to localhost (edit hosts file)
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# ... (comments omitted) ...
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
127.0.0.1 socket.fmsoft.net2
4
4. Test with a local HyperServer instance
create folder 
copy hyperserver binaries 
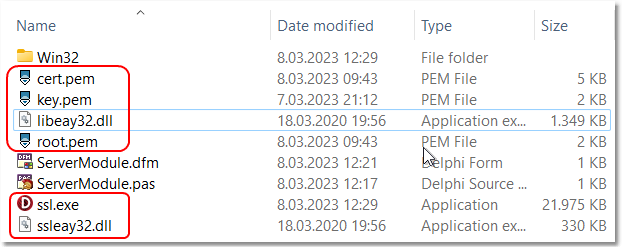
copy ssl dlls and certs
object TUniHyperSSL
SSL.Enabled = True
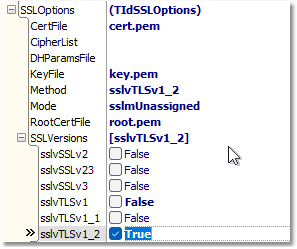
SSL.SSLOptions.RootCertFile = 'root.pem'
SSL.SSLOptions.CertFile = 'cert.pem'
SSL.SSLOptions.KeyFile = 'key.pem'
SSL.SSLOptions.Method = sslvTLSv1_2
SSL.SSLOptions.SSLVersions = [sslvTLSv1_2]
SSL.SSLOptions.Mode = sslmUnassigned
SSL.SSLOptions.VerifyMode = []
SSL.SSLOptions.VerifyDepth = 0
SSL.SSLPort = 0
end
copy demo exe
[hyper_server]
binary_name=FishFacts.exe
system tray icon 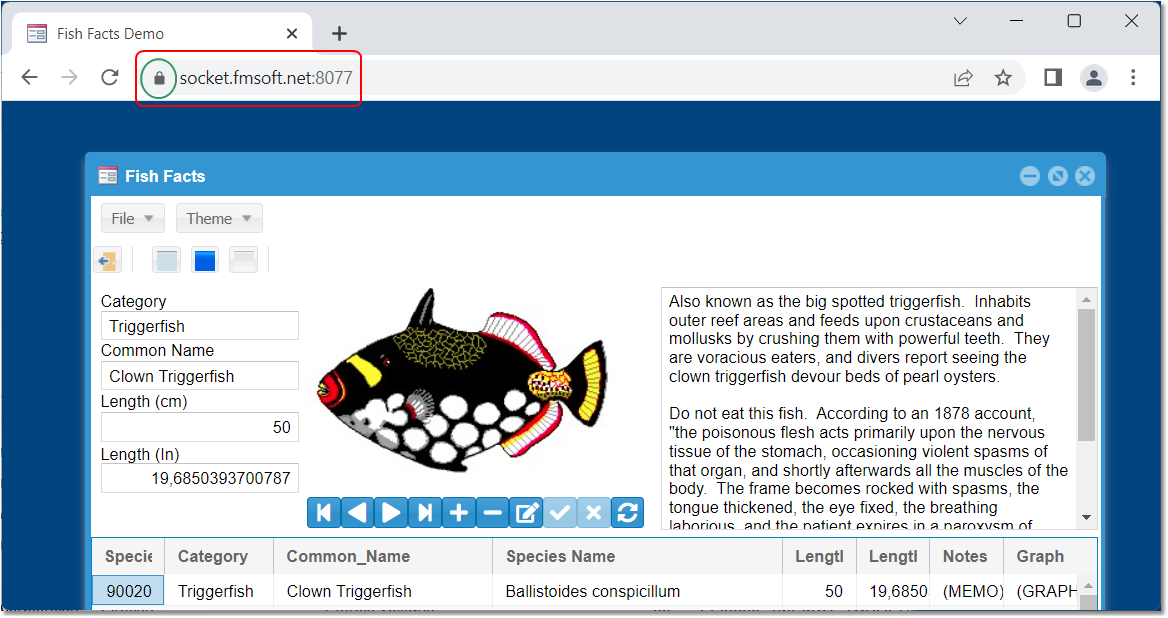
fishfacts running 
fishfacts running 2 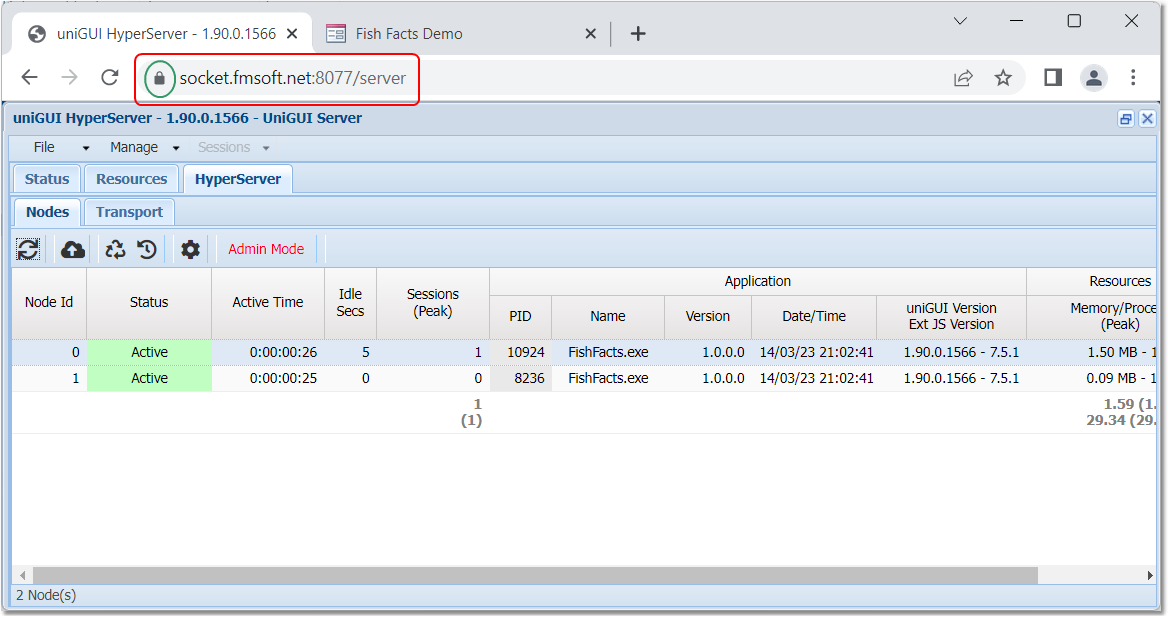
fishfacts running 3